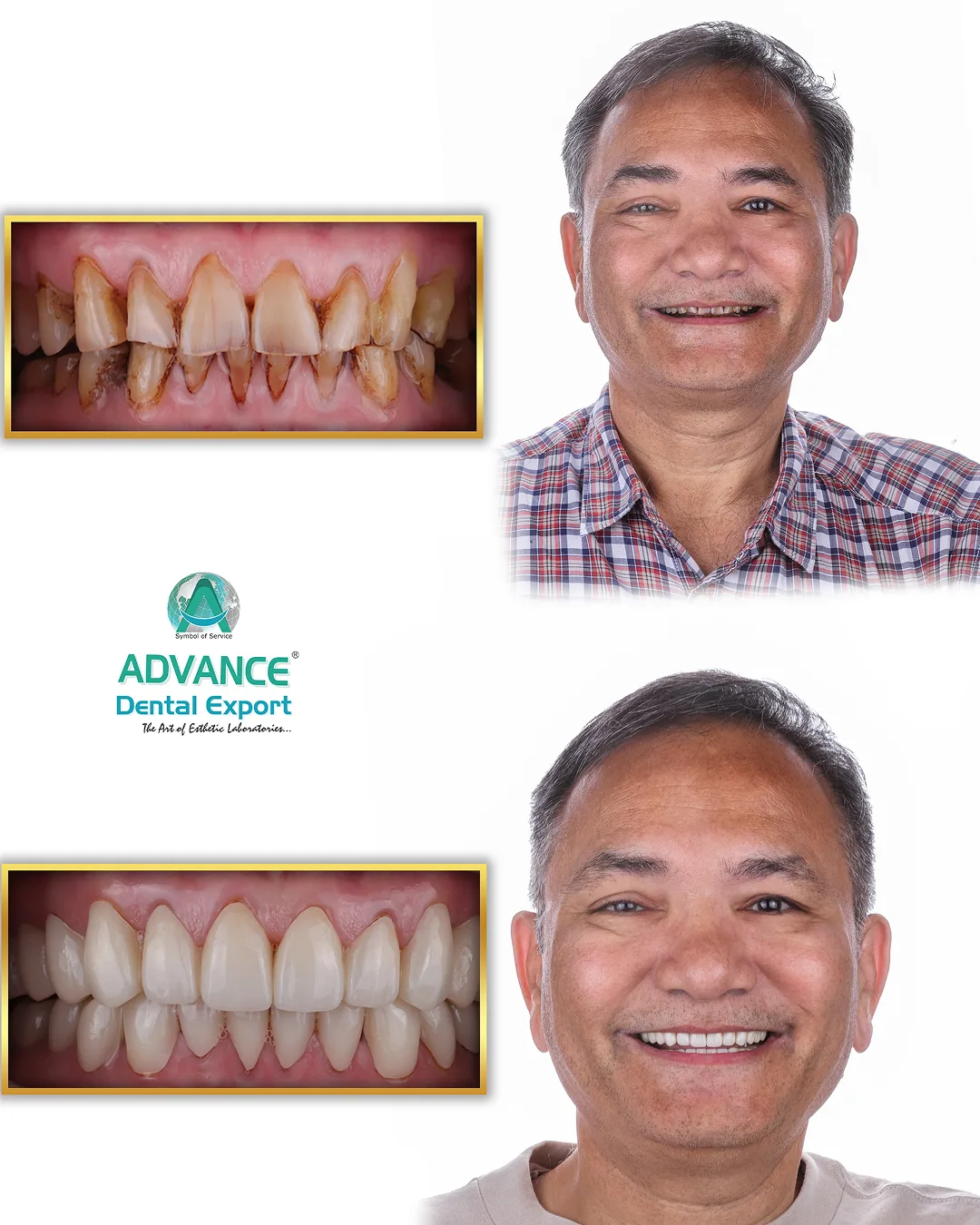
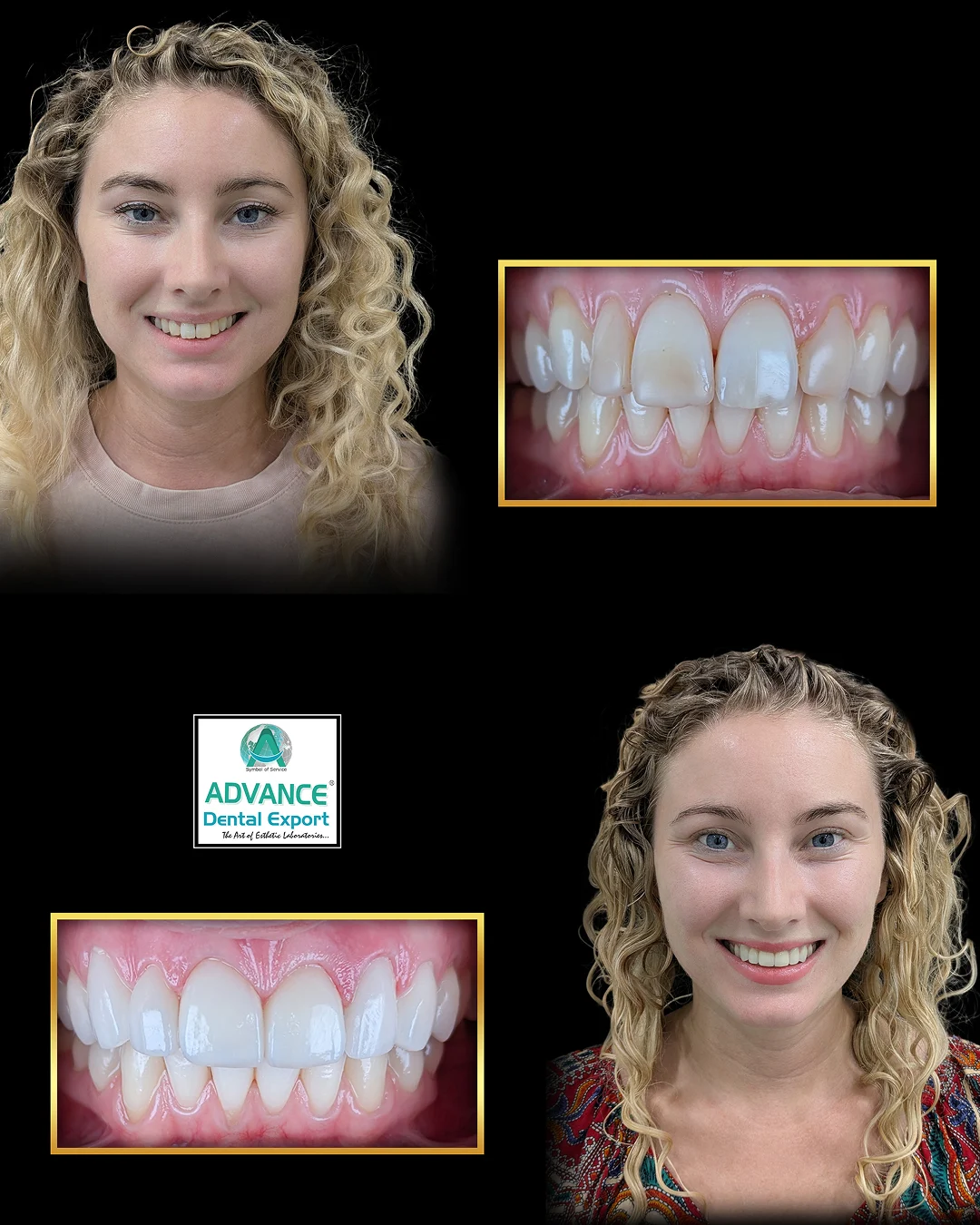
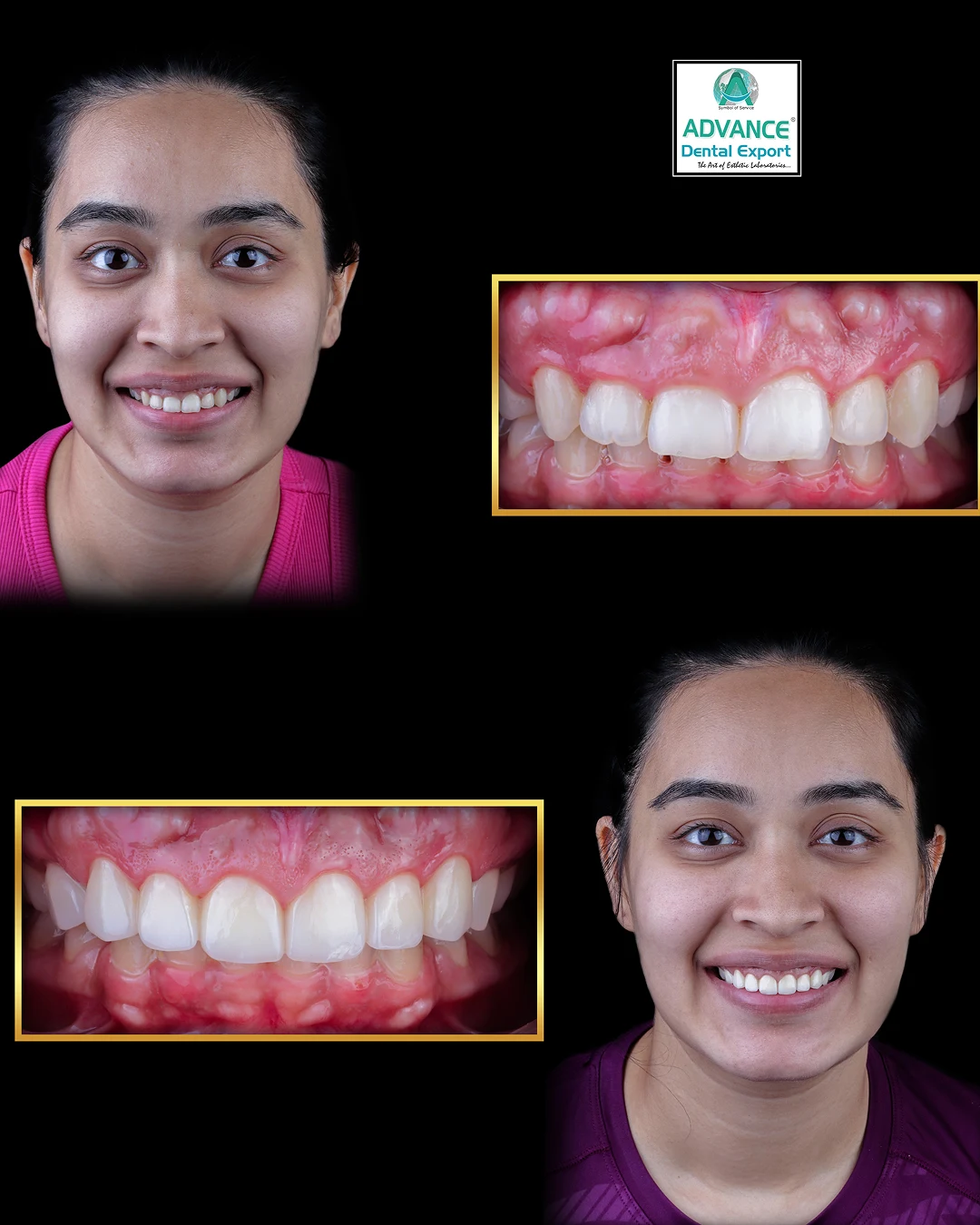
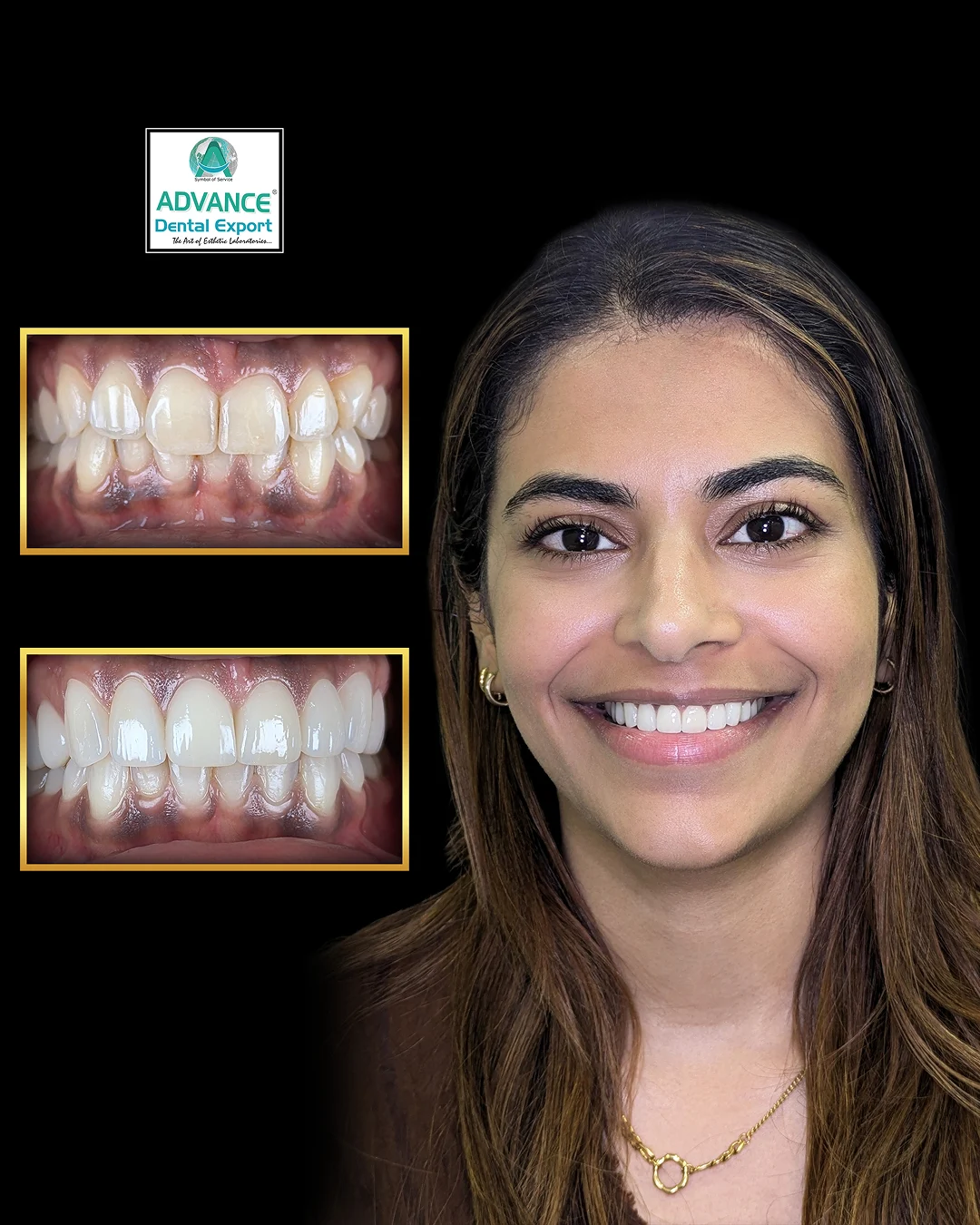
Imagine a world where your dentist can craft a custom dental crown or aligner while you wait—no molds, no multiple appointments, just precision and speed. Welcome to the realm of 3D printing in dentistry , a groundbreaking technology that's transforming how dental care is delivered.
But what exactly does this mean for you as a patient or dental professional? How does a digital file evolve into a tangible dental solution? And why should you care?
Let’s learn what 3D printing is in dentistry. We’ll delve into a detailed guide to dental 3D printing.
What is 3D Printing in Dentistry?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a cutting-edge technology that enables dental professionals to create precise, customized dental prostheses directly from digital files. Unlike traditional subtractive methods, where material is removed to shape the final product, 3D printing builds up layers of material to form the desired object.
In the dental context, 3D printing involves using computer-aided design (CAD) software to generate a digital model of a dental prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or aligner. This model is then sent to a 3D printer, which fabricates the appliance layer by layer using materials like photopolymer resins or biocompatible plastics. The result is a highly accurate and customized dental solution tailored to the patient's unique anatomy.
The journey of 3D printing began in the 1980s, with Charles Hull's invention of stereolithography (SLA) in 1986, which laid the foundation for modern 3D printing technologies in the dental industry. Initially, these technologies were used for rapid prototyping across various industries. In dentistry, the integration of CAD/CAM systems in the late 20th century marked a significant milestone, allowing for digital impressions and the precise fabrication of dental restorations. Over time, advancements in 3D printing materials and techniques have expanded its applications in dentistry, including the creation of surgical guides, orthodontic models, and implant components.
Today, 3D printing is increasingly adopted in dental practices worldwide. According to a report by Research and Markets, the market for 3D printing in dentistry is projected to grow by an average of 12.6% per year until 2035. This growth is driven by the technology's ability to produce highly accurate, patient-specific dental solutions efficiently and cost-effectively. While still not ubiquitous in all dental offices, early adopters report significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction, indicating a promising future for 3D printing dentistry.
How Does Dental 3D Printing Work?
Dental 3D printing is a streamlined, digital process that transforms a patient's unique dental anatomy into a customized appliance. This process involves three main stages: Data Acquisition, Design, and Printing.
Explore Our Restorations
Data Acquisition: Capturing the Impressions
The journey begins with obtaining precise digital impressions of the patient's oral structures. This is achieved using:
- Intraoral Scanners: Handheld devices that capture detailed 3D images of the teeth and gums.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): Provides 3D X-ray images, offering comprehensive views of the dental and skeletal structures.
These digital impressions replace traditional molds, enhancing accuracy and patient comfort. The resulting data serves as the foundation for the next steps in the process.
Design: Crafting a Customized Solution
Once the digital impressions are obtained, the next step is designing the dental appliance:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Specialized software is used to create a detailed 3D model of the dental appliance, such as a crown, bridge, or aligner.
- Customization: The design is tailored to fit the patient's unique anatomy, ensuring optimal function and comfort.
This digital design process allows for precise adjustments and modifications before the actual fabrication begins.
Printing: From Digital to Physical
The final step involves transforming the digital design into a physical dental appliance:
- 3D Printing Technologies: Various methods, such as Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP), are employed to build the appliance layer by layer.
- Materials Used: Biocompatible resins and plastics are commonly used, selected based on the specific requirements of the dental appliance.
This additive manufacturing process ensures high precision and the ability to produce complex geometries that traditional methods may not achieve. By integrating these advanced technologies, dental 3D printing offers a streamlined, efficient, and patient-friendly approach to creating customized dental solutions.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
Dental 3D printing has revolutionized various aspects of dental care, offering precise, customized, and efficient solutions. Below are some of the most impactful applications:
1. Custom Dental Crowns, Bridges, and Dentures
3D printing enables the rapid production of dental restorations tailored to individual patients. Materials like photopolymer resins are used to create crowns, bridges, and dentures that fit seamlessly, reducing the need for multiple fittings. This not only enhances patient comfort but also shortens treatment times.
2. Clear Aligners and Retainers
Orthodontics has benefited significantly from 3D printing. Transparent aligners and retainers can be produced with high precision, ensuring a better fit and comfort for patients. These appliances are designed based on digital impressions, allowing for a more personalized treatment approach.
3. Surgical Guides for Implantology
In implant dentistry, 3D-printed surgical guides help in implant placement . These guides are created using detailed imaging data, ensuring that implants are positioned correctly, which is crucial for the success of the procedure.
4. Bite Splints and Night Guards
For patients suffering from bruxism or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, 3D printing offers the ability to create custom bite splints and night guards. These devices are designed to fit the patient's unique dental anatomy, providing better protection and comfort.
5. Dental Models for Education and Planning
3D-printed dental models serve as valuable tools for education and treatment planning. They allow dental professionals to visualize complex cases, practice procedures, and communicate effectively with patients about their treatment options.
These applications illustrate how 3D printing is transforming dental practices, offering solutions that are not only efficient but also tailored to the individual needs of patients.
Looking for a trusted lab partner? Get high-precision restorations from Advance Dental Export
Getting Started with Dental 3D Printing
Embarking on the journey of dental 3D printing can seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it becomes an exciting opportunity to enhance your practice. Here's a beginner-friendly roadmap to help you integrate 3D printing into your dental workflow.
Essential Equipment for Dental 3D Printing
To begin, you'll need to invest in the following core components:
- 3D Printer: Choose a printer compatible with dental resins.
- Intraoral Scanner: Devices like the iTero Element or Medit i500 capture precise digital impressions.
- CAD CAM in Dentistry : Software such as exocad or 3Shape Dental System allows for the design of dental restorations.
- Post-Processing Equipment: Items like wash stations and curing lights are essential for finishing printed models.
The initial investment for a complete setup can range from $20,000 to $30,000, depending on the quality and features of the equipment.
Training and Learning Resources
Proper training is crucial to effectively utilize dental 3D printing technology. Consider the following resources:
- Institute of Digital Dentistry (iDD): Offers free CE/CPD courses covering various aspects of dental 3D printing, from scanning to material processing.
- The MOD Institute: Provides foundational courses like "3D Printing Foundations" and "Master Scanning and 3D Printing in Your Dental Clinic."
- Formlabs Dental Academy: Features guided learning sessions and courses to help you master digital dentistry workflows.
Additionally, hands-on workshops and webinars can provide practical experience and insights.
Workflow Tips for Beginners
To ensure a smooth integration of 3D printing into your practice:
- Start with Simple Applications: Begin by printing dental models, surgical guides, and splints.
- Build a Patient Library: Regularly scan patients to create a digital archive, facilitating future treatments.
- Collaborate with Experienced Professionals: Engage with online communities and forums to share experiences and seek advice.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest advancements in materials and techniques to continually improve your practice.
By following this roadmap, you can confidently embark on your journey into dental 3D printing, enhancing your practice's capabilities and offering innovative solutions to your patients.
Final Thoughts
Dental 3D printing isn't just a passing trend—it's reshaping the way we approach dental care. From personalized crowns to precise surgical guides, this technology empowers dental professionals to deliver faster, more accurate, and comfortable treatments. Whether you're a dentist looking to innovate or a patient seeking cutting-edge care, embracing 3D printing is a step toward a brighter, more efficient dental future.