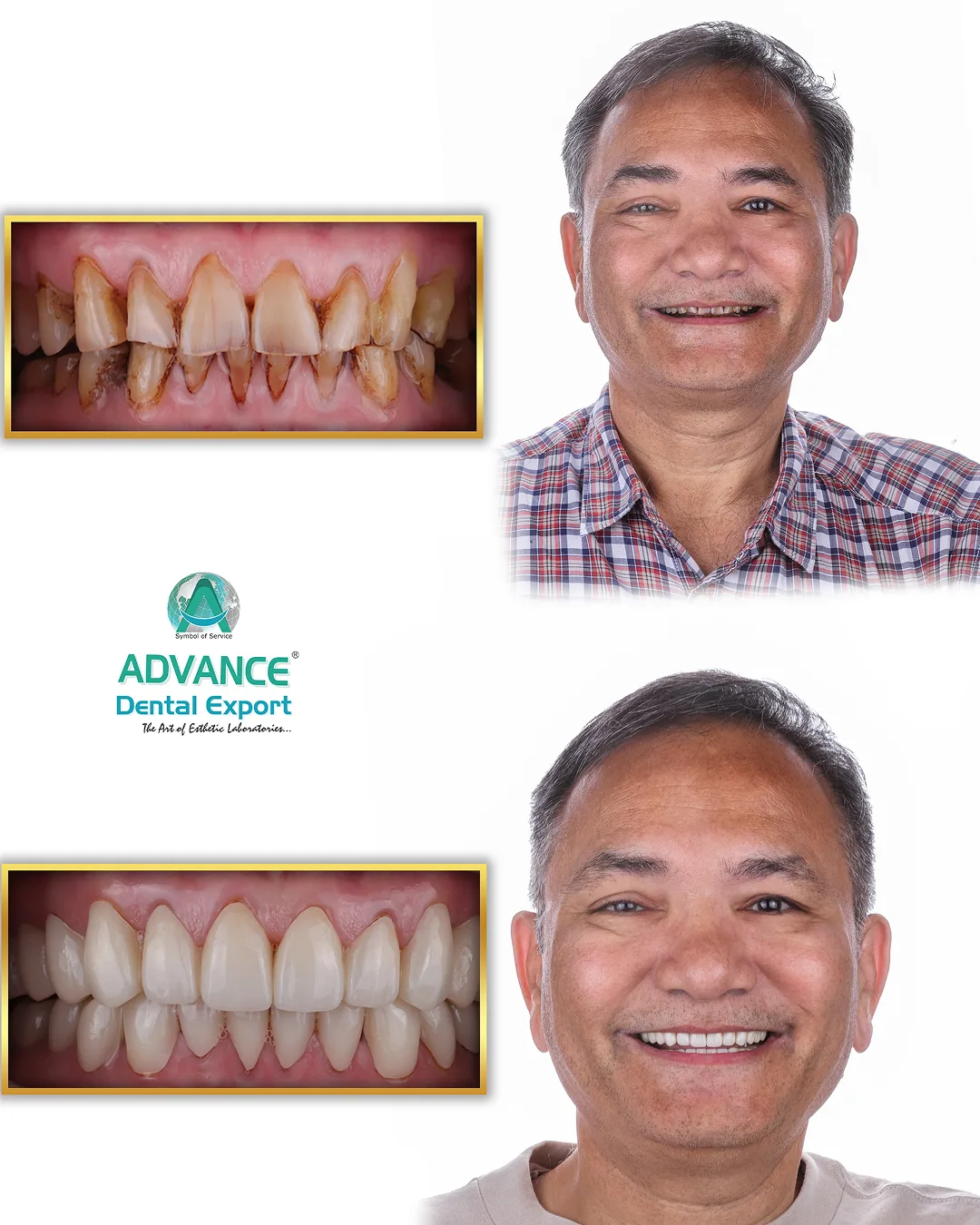
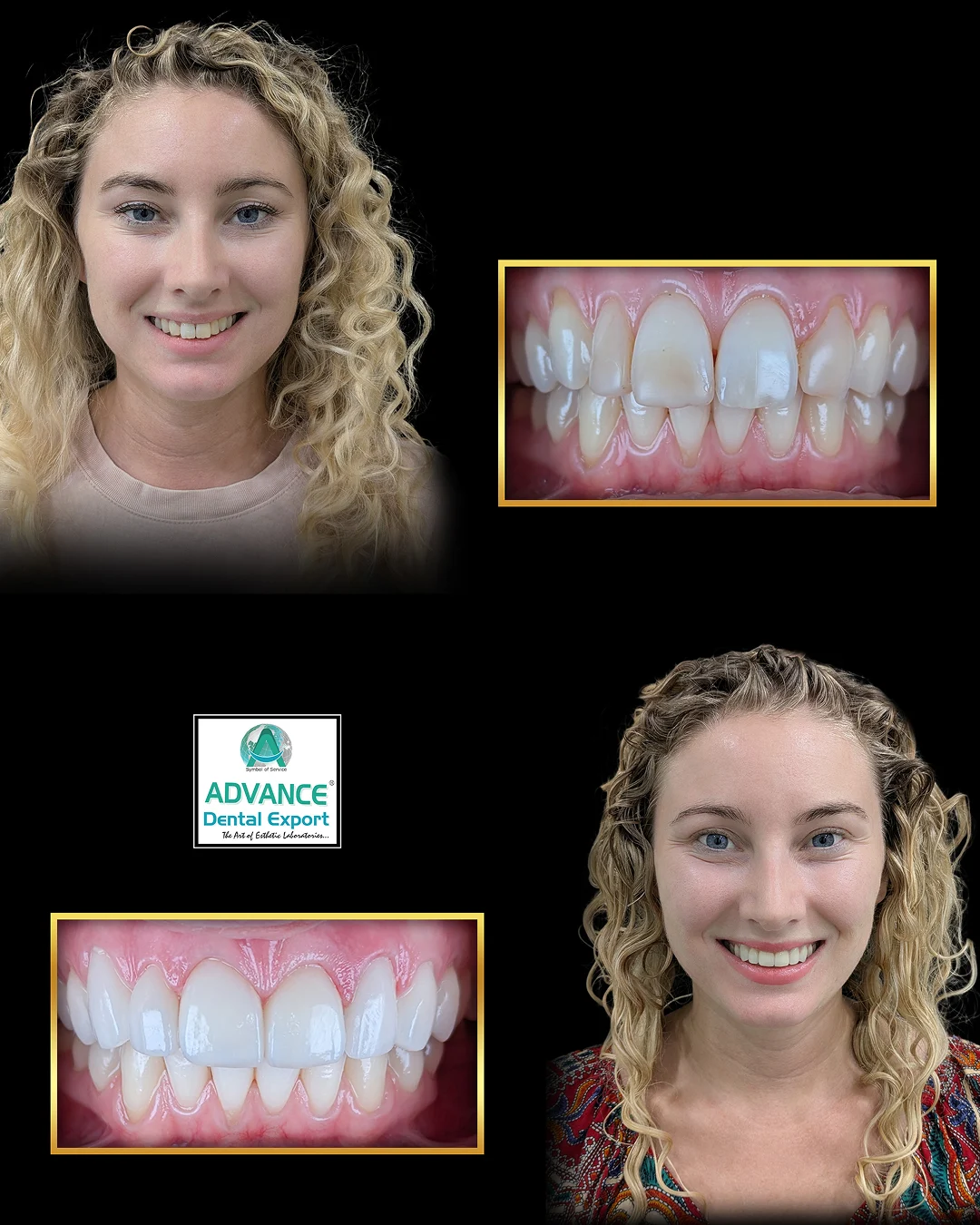
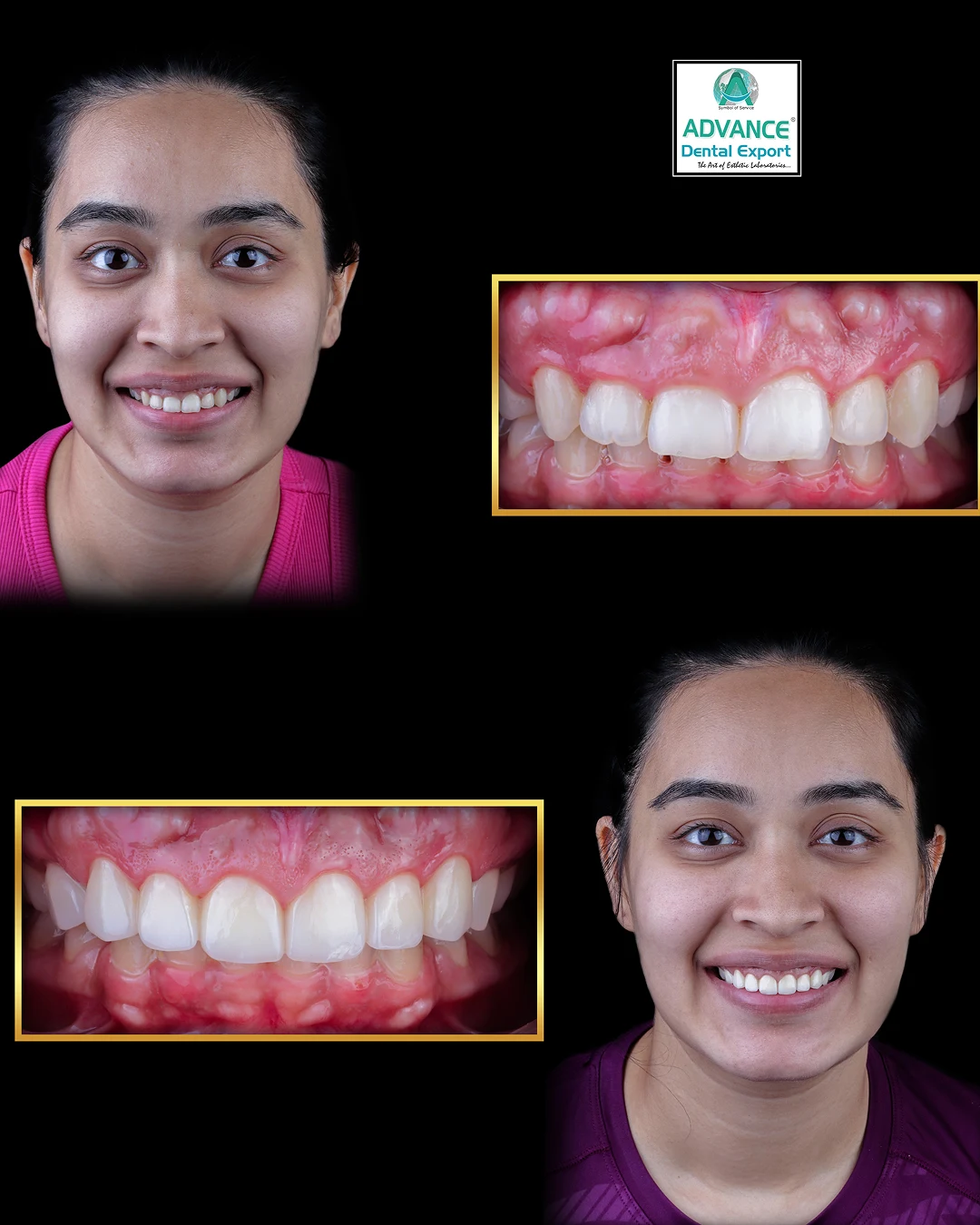
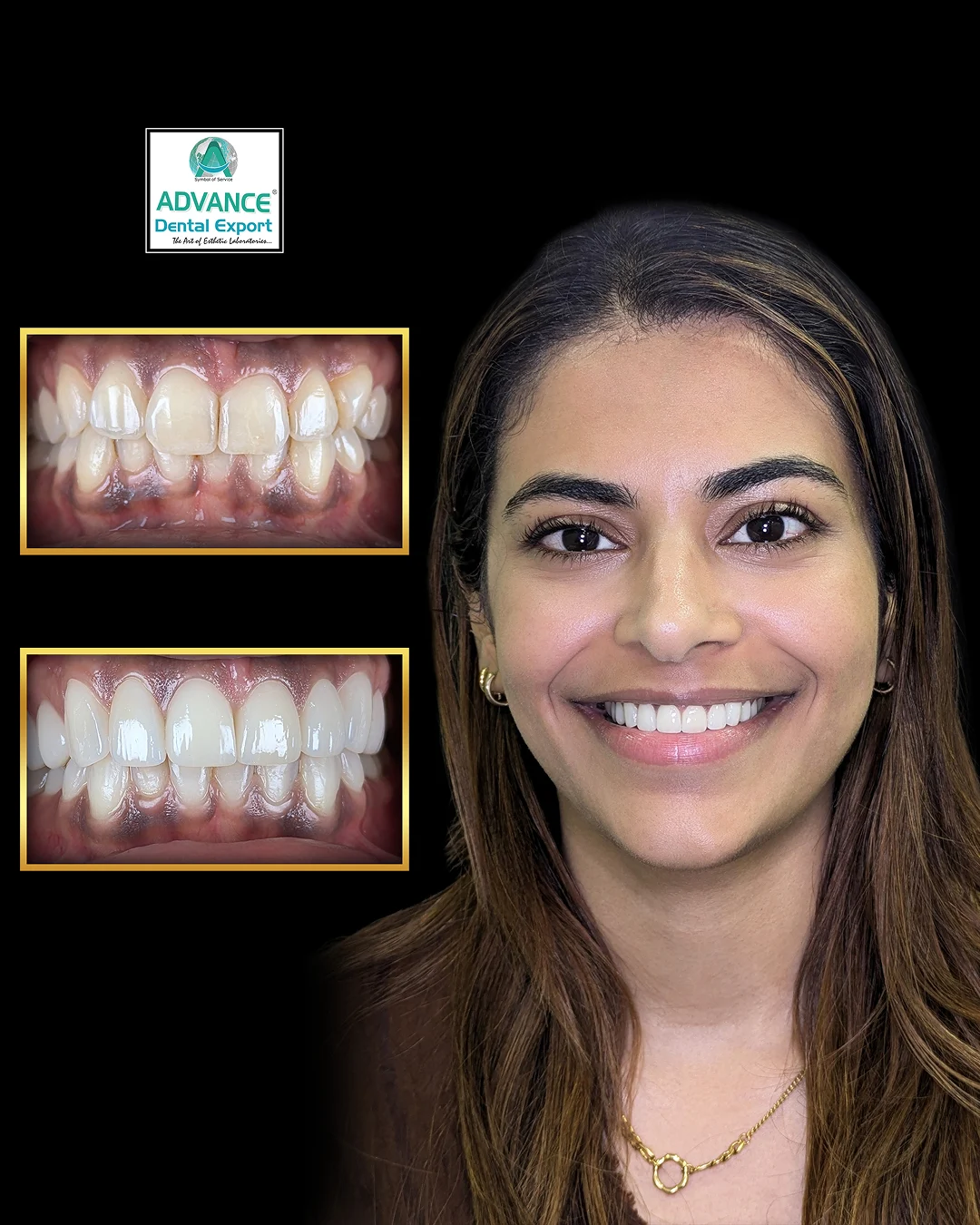
Dentistry has entered a new digital era. Gone are the days of solely relying on messy impressions and weeks-long lab work. Today’s modern dentistry integrates cutting-edge digital tools that make treatments faster, more accurate, and more comfortable for patients. This transformation is known broadly as digital dentistry .
Digital modern dentistry encompasses everything from taking digital dental impressions with 3D scanners to designing restorations on a computer and manufacturing them using milling machines or 3D printing. The result is a streamlined workflow that benefits both dentists and patients, especially in tech-forward practices (including many in India) looking to elevate their quality of care.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore digital dentistry in contemporary practice and dive into its core components: advanced scanning equipment, CAD/CAM design, 3D printing, and the rise of the digital dental lab.
Digital Dentistry in Modern Dental Practice
Digital dentistry refers to the use of computer-driven and AI technologies and devices in dental procedures, rather than traditional mechanical methods. Its purpose is to enable dental professionals to deliver treatment with the help of software and hardware tools, improving efficiency and outcomes.
In practical terms, digital dental technology encompasses a range of innovations – from digital X-rays and intraoral scanners to CAD/CAM milling units and AI-based planning software. These tools collectively have a transformative role in modern dentistry, making procedures more precise and patient-friendly than before.
Today, we can take virtual impressions, fabricate restorations in one visit, and even plan surgeries on a computer. Over time, dentists have invented and adopted numerous digital solutions to optimise treatment, though adoption is still ongoing. In fact, research by 3Shape noted that as of a couple of years ago, around 85% of dental clinics worldwide were still taking impressions the old way – with trays and putty.
In countries like the U.S., nearly one-third of clinics have intraoral scanners, while in India, the figure is smaller (estimated between 1% and 15%) but growing fast. The consensus in the industry is clear: the future of dental care is digital , and adoption is accelerating every year.
For a dentist, understanding the role of digital dentistry means recognising how these technologies can enhance every aspect of practice – from diagnosis (e.g., using digital imaging and CAD software for treatment planning) to execution (e.g., milling a crown on-site).
Embracing digital tools isn’t just about staying on the cutting edge; it’s about providing higher-quality care that today’s patients expect. Let’s break down the core components of modern dentistry and see how they are revolutionising dental treatment.
Scanning Equipment in Digital Dentistry
One of the foundational technologies in computer-aided dentistry is advanced scanning equipment. Digital scanners capture precise 3D images of teeth and oral structures, replacing many traditional diagnostic methods. Scanners can be broadly categorised by their use case: those used in clinics (patient-facing) and those used in labs. In practice, this mainly refers to two types of scanners: intraoral scanners (IOS) and lab/desktop scanners.
Intraoral scanners – essentially digital dental scanners – have changed the game for impression taking. Instead of filling a tray with gooey alginate and waiting minutes for it to set in a patient’s mouth, a dentist can now use a small handheld camera wand to create a digital dental impression in minutes.
The scanner rapidly captures the contours of the teeth and gums, stitching together images into a highly accurate 3D model of the patient’s mouth. This 3D model appears instantly on screen, allowing both the dentist and patient to visualise the situation.
Overall, the intraoral scanner in dentistry has become an indispensable tool – it captures details the naked eye would miss and can even help detect issues like early caries when combined with certain software.
Dental cone-beam CT (CBCT) scanners are another form of digital scanning equipment commonly used in clinics. These 3D imaging machines take detailed X-rays of the jaws and skull, producing a volumetric image that dentists use for implant planning, orthodontic assessments, detecting hidden pathology, and more.
Real-world impact: If you’ve ever had a crown made the old way, you know it involved an uncomfortable impression, a temporary crown, and a two-week wait while the model was mailed to a lab. With digital scanning, a dentist can take a full-mouth 3D scan in a few minutes, instantly email the digital file to the lab, or even design the crown in the office.
CAD/CAM in Digital Dentistry
After capturing data with scans, the next step in the digital workflow is CAD/CAM – Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing. CAD/CAM in digital dentistry refers to using software to design restorations or appliances, and then using automated machines to manufacture them. This technology allows dentists and labs to go from concept to final product with unprecedented speed and precision.
In day-to-day conversation, “CAD/CAM” often encompasses the entire process: from scanning a patient to digitally designing the solution, to milling or printing the result. The beauty of CAD/CAM is that it can enable single-visit treatments for many restorations.
For example, with a chairside CAD/CAM system, a dentist can prepare a tooth, take a digital scan, design a crown on the computer, and mill it right in the office – all within an hour or two. This way, dentists can now complete a ceramic inlay or crown in 50–90 minutes, whereas with traditional methods, that process took a day or more.
Explore Our Restorations
The CAD software provides powerful tools to virtually sculpt crowns, bridges, dentures, and more with incredible accuracy. Because it’s digital, the design can be adjusted in real-time, guided by factors like the patient’s bite, esthetics, and the dentist’s input.
In the lab context, CAD/CAM allows technicians to design complex frameworks or implant prosthetics that would be arduous to do by hand, streamlining even the most complex cases.
3D Printing in Dentistry
Another revolutionary component of advanced dental technology is 3D printing (additive manufacturing) . 3D printing in dentistry has quickly moved from a novelty to a mainstream tool in both dental labs and forward-thinking clinics. This technology builds objects layer by layer from materials like resin or metal, based on digital 3D models. It opens up incredible possibilities for custom dental appliances produced rapidly and with great accuracy.
Dentists and labs can use 3D printing to produce a wide variety of items: crowns and bridges, custom implant abutments, dentures, dental models, clear aligners, retainers, occlusal splints, surgical guides for implant surgeries, custom trays, and more. Essentially, if it can be designed digitally, it can likely be printed.
For example, orthodontic aligner companies often 3D print moulds of each tooth position and then fabricate clear aligners on those models. Implantologists might 3D print a precise surgical guide that directs their drill to the exact angulations and depths required for implant placement. Prosthodontists are now experimenting with 3D printing full dentures, including both the denture base and teeth, with resins that look remarkably life-like.
One major appeal of 3D printing is speed and cost-effectiveness. A printer can create models or parts overnight or even within an hour or two, which is much faster than some traditional lab processes. As noted by the IDA, 3D printers allow personalised dental items and models to be made more quickly and often more affordably than with traditional methods.
The accuracy and customisation offered by 3D printing are also noteworthy. Because the process follows the digital design exactly, the end product can be extremely precise. Appliances like night guards or dentures are fitted with minimal adjustments, and if an error does occur, you simply adjust the digital model and reprint – no need to start from scratch manually.
In summary, 3D printing works hand-in-hand with CAD/CAM and scanning as part of the digital workflow . The future of 3D printing in dentistry is bright – it’s expected to keep growing rapidly as a core fabrication method, complementing the precision of digital design with on-demand production.
Rise of Digital Dental Labs and Workflow
The rise of digital dentistry has also given birth to the digital dental lab – laboratories that heavily leverage digital workflows to fabricate restorations and appliances.
Traditionally, dental labs were analogue operations involving plaster models, waxing, casting, and lots of handcrafting. In contrast, a high-tech dental lab uses technologies like 3D scanners, CAD software, milling machines, and 3D printers to fulfil dental prescriptions. Partnering with a digital lab can significantly improve a practice’s efficiency and the quality of lab work.
One of the biggest advantages of a digital lab workflow is streamlined communication between the clinic and lab. When a dentist uses a digital impression, it can be sent to the lab electronically within minutes of capturing it.
Digital labs also contribute to higher accuracy. Since they receive a precise digital model, problems like impression distortions are eliminated. Digital files don’t suffer from material shrinkage or shipping damage, so the lab works with a replica of the patient’s anatomy.
Moreover, digital dental labs also enable new levels of collaboration. With traditional workflows, if there was an issue with a case, the lab had to call the dentist and maybe send the model back or have the dentist send a new impression.
For dentists in India and elsewhere considering moving from traditional to digital dentistry, working with a fully digital dental lab can be a great way to start. Even if you haven’t invested in milling or printing yourself, you can take digital impressions and send them to a lab that will handle the CAD/CAM fabrication .
Many labs now brand themselves as “digital dental labs” and market benefits like enhanced consistency, faster deliveries, and the ability to handle complex cases via digital design. They often provide guidance on how to send files and may even help dentists select an intraoral scanner that integrates well with their system.
Ultimately, digital labs offer a win-win: improved lab work quality for dentists and increased efficiency and profitability for the labs themselves. Practices that “go digital” find that their lab partnerships improve significantly, with fewer errors and happier patients as a result.
Digital Restorative Dentistry
When we talk about digital restorative dentistry, we’re referring to how digital tools have revolutionised the process of restoring teeth – from fillings and crowns to bridges, veneers, and dentures. Essentially, it’s the application of digital workflows (scanning, CAD, CAM, 3D printing) to the practice of repairing or replacing teeth. The impact on restorative care has been profound: procedures that once took multiple long appointments can now often be completed in a single visit, with greater precision and patient comfort.
Consider the traditional vs digital experience for a common restorative procedure, like getting a crown:
- Conventional method: The dentist would prepare the tooth and take a physical impression using a tray filled with paste. The patient might gag or feel uncomfortable during this process. The impression would then be sent to a lab. The patient goes home with a temporary crown and waits perhaps 1–2 weeks for the permanent one to be made. At the second visit, the temporary is removed and the new crown is fitted, with adjustments as needed. If the fit was off or the shade wrong, that could mean further delays or remakes.
- Digital method: The dentist prepares the tooth and then uses an intraoral scanner to take a digital impression – quickly and comfortably without gooey material. The 3D image of the tooth is immediately available. Using CAD software, the dentist designs the crown while the patient watches or relaxes. In many cases, the dentist can then mill the crown right in the office (or send the file to a milling unit or printer). Within the same appointment – often within an hour or two – the permanent crown is ready to be bonded in place. Often, the entire treatment is completed in one visit, with no need for a temporary restoration or a second injection of anaesthesia. The patient leaves with their final crown that day, avoiding the inconvenience of multiple appointments.
In summary, digital restorative dentistry streamlines the journey of fixing or replacing teeth. It enhances each step: scanning makes diagnosis and impressions quick and accurate, CAD/CAM makes design and fabrication efficient and precise, and digital collaboration ensures any issues are caught early.
Looking for a trusted lab partner? Get high-precision restorations from Advance Dental Export
Benefits of Digital Dentistry
Digital dentistry offers numerous benefits over traditional techniques, fundamentally improving how dentists deliver care. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Higher Precision & Accuracy: Digital tools (scanners, CAD software) capture and reproduce dental anatomy with microscopic accuracy.
- Shorter Treatment Times: Dental impressions take a few minutes with digital dentistry instead of 15+ minutes for traditional moulds.
- Improved Patient Comfort: Digital scanning is far more comfortable and less invasive. Overall, treatments become less stressful.
- Streamlined Workflow & Efficiency: Digital workflows remove many manual steps that were time-consuming and error-prone.
- Predictable, High-Quality Outcomes: With digital simulation, dentists can plan treatments virtually and identify issues in advance.
- Data Storage & Replicability: Digital impressions and designs are stored electronically, which means no need to keep boxes of plaster models.
- Cost Effectiveness in the Long Run: While initial investment in digital equipment can be high, the efficiency and savings on materials often pay off over time.
In summary, digital dentistry enhances expertise, efficiency, and patient trust – hallmarks of excellent dental care. It aligns perfectly with the principles of quality and accuracy that dental professionals strive for, which is why more and more clinics are making the digital transition each year.
Embracing Digital Dentistry: Tips for Dentists
Integrating digital technology into your practice can seem daunting, but it’s easier now than ever – and almost always worth the effort. Here are some practical tips for dentists (in India or anywhere) looking to embrace digital dentistry:
- Start with the Basics – If you’re new to digital tools, an intraoral scanner is often the best first investment. It immediately improves the patient experience and the quality of your impressions. Many dentists find that once they switch to digital dental scanners for impressions, they never want to go back.
- Leverage a Digital Dental Lab Partnership: You don’t need to buy a milling machine or 3D printer on day one. Digital dental labs like Advance Dental Export can do the heavy lifting for CAD/CAM work. By working with them, you’ll deliver better restorations to your patients without having to manage all the fabrication yourself.
- Stay Updated and Network: Digital dentistry is a dynamic field. Keep up with the latest trends – whether it’s AI in radiology, new resin materials for 3D printing, or software upgrades that make design easier.
Ultimately, transitioning to high-tech dentistry is about enhancing the care you provide. It might require some upfront cost and training, but the payoff is a practice that runs smoothly, and a professional life made a bit easier by technology.
Conclusion
Digital dentistry is more than a buzzword – it represents a fundamental shift in how dental care is delivered. By incorporating technologies like intraoral scanners, CAD/CAM systems, and 3D printing, modern dentistry has become faster, more precise, and more patient-friendly.
In India and around the world, we’re witnessing a digital transformation in dentistry that is only picking up speed. Industry data suggests that the coming years will see a sharp rise in digital workflow adoption, as costs for technology decrease and the return on investment becomes indisputable. Moreover, patient demand is driving this change: people increasingly prefer clinics that use advanced techniques, associating them with higher quality care. The role of digital dentistry in improving patient satisfaction and outcomes cannot be overstated – it truly elevates the dental experience on all fronts.
Don’t let your practice get left behind – embrace the digital dentistry revolution and experience the benefits for yourself and your patients.
FAQs
- What is digital dentistry?
Digital dentistry refers to the use of advanced digital technologies and computer-controlled devices to perform dental procedures instead of traditional mechanical tools. This includes things like 3D imaging, intraoral scanning, CAD/CAM design software, and 3D printing.
- How is CAD/CAM used in digital dentistry?
CAD/CAM stands for Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing. In digital dentistry, CAD/CAM is used to design and create dental restorations or appliances digitally. This can be done in-office (e.g., same-day crowns milled chairside) or in a dental lab. The use of CAD/CAM makes the process much faster and often more accurate than hand-made techniques.
- What are the benefits of digital dentistry for dentists and patients?
Digital dentistry offers numerous benefits:
Greater accuracy: Digital impressions and CAD designs are extremely precise, leading to restorations that fit better with minimal adjustments.
Time efficiency: Many procedures can be done faster. Turnaround times for lab work shrink from weeks to days or hours, and treatments like crowns or bridges can sometimes be completed in a single appointment.
- What does an intraoral scanner do, and is it better than traditional impressions?
An intraoral scanner is a handheld digital device that captures a direct 3D image of a patient’s teeth and gums. It projects light (or uses laser/photography) to map the surfaces inside the mouth and creates a digital model (often in full colour) on the computer. Essentially, it takes a digital dental impression.