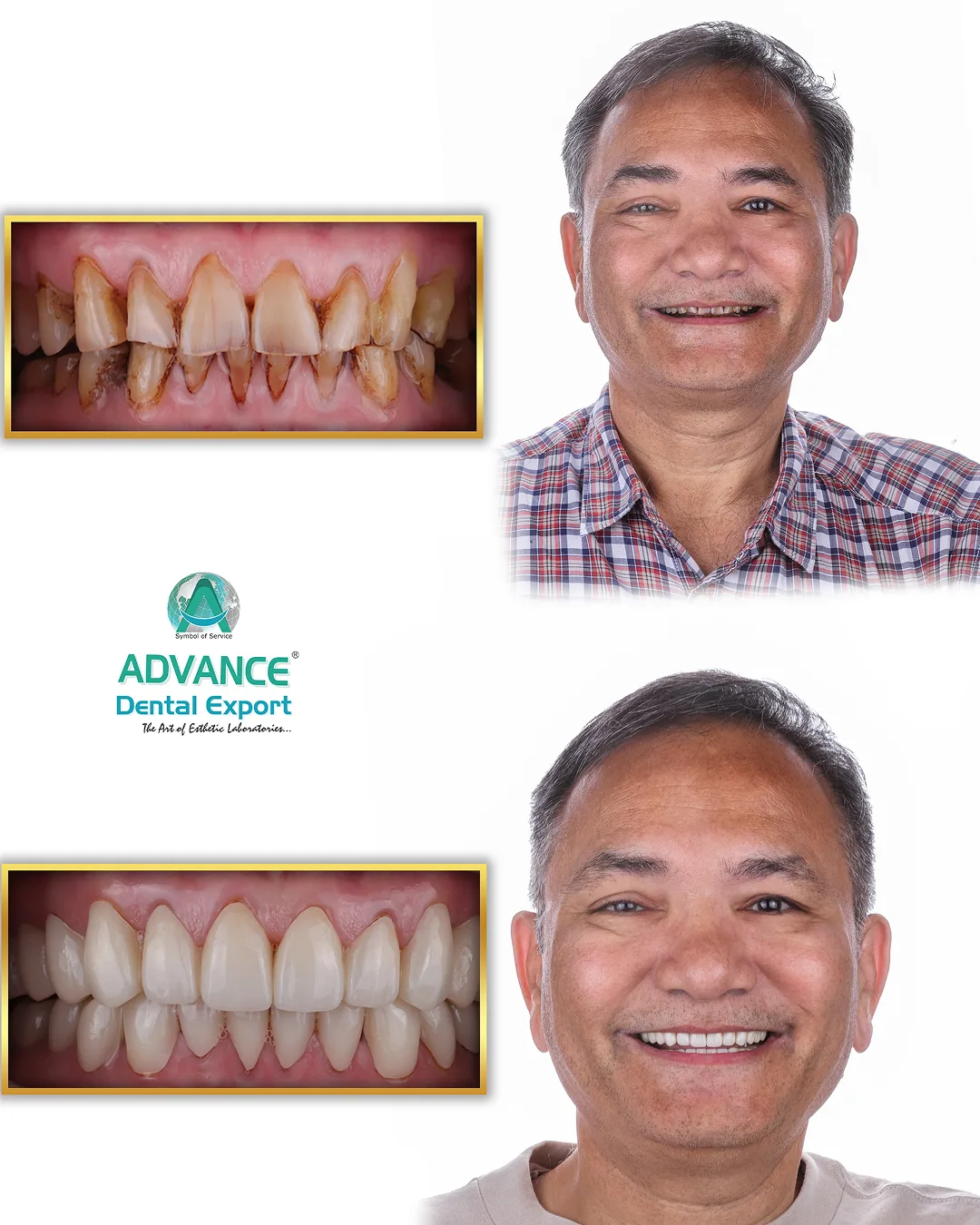
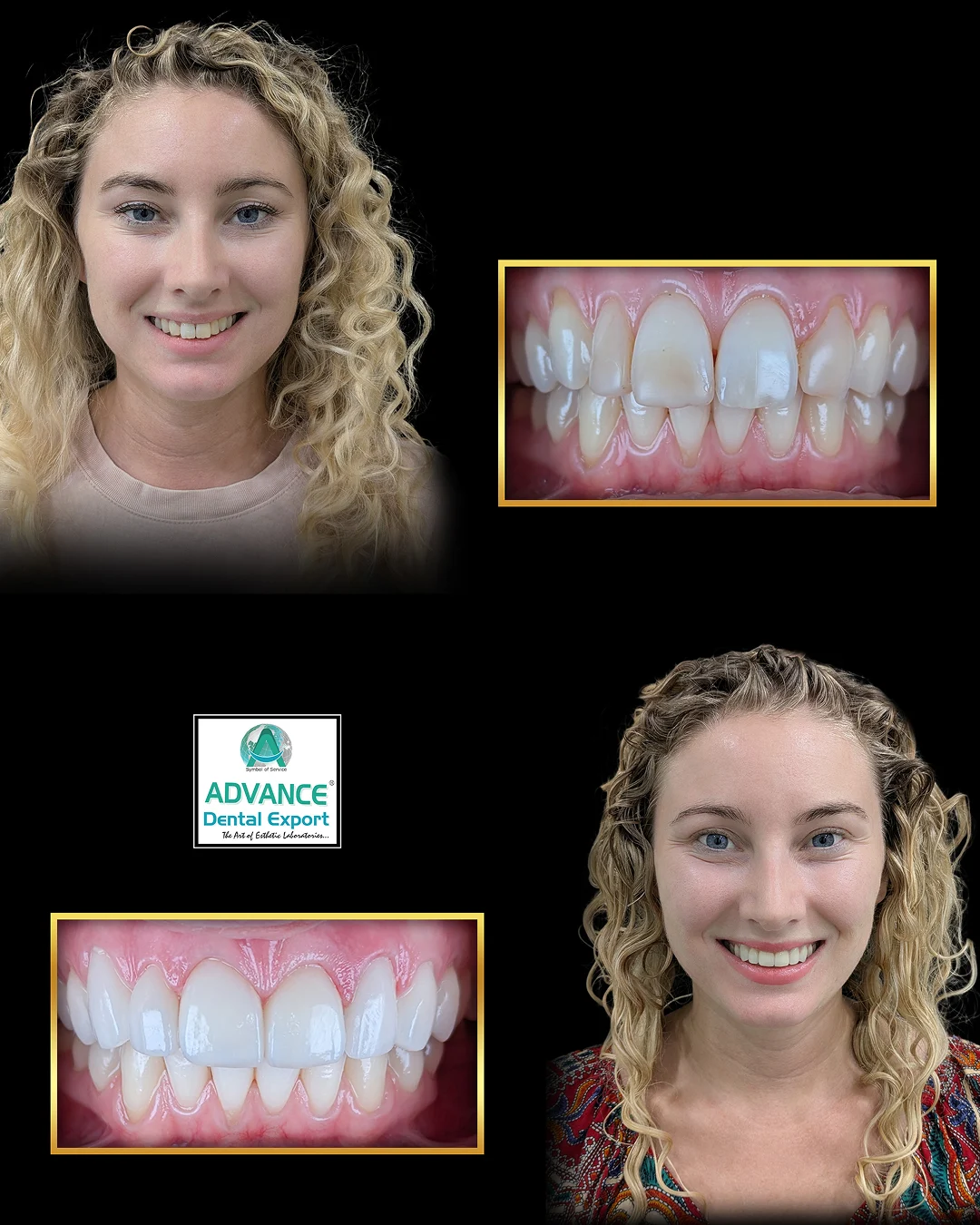
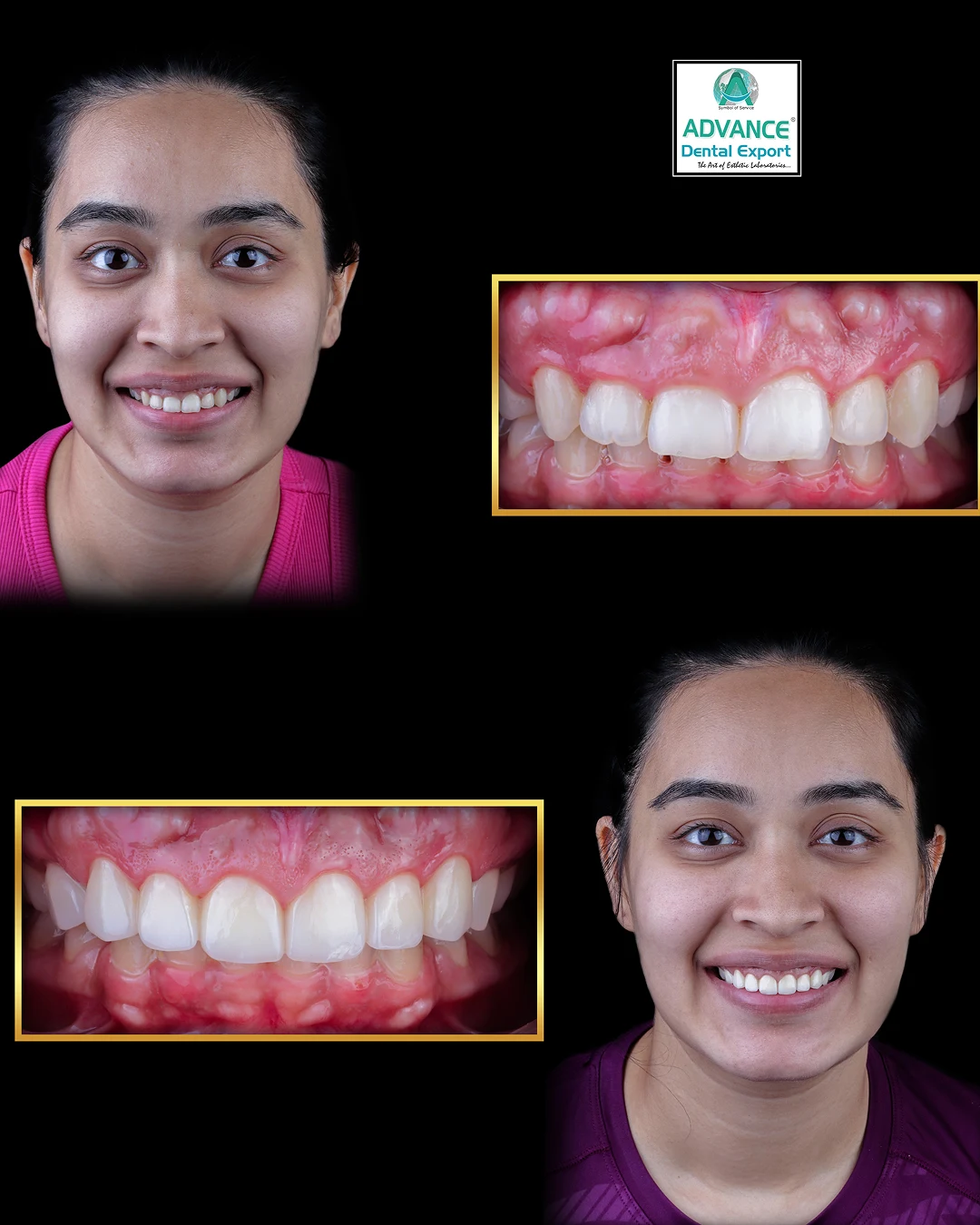
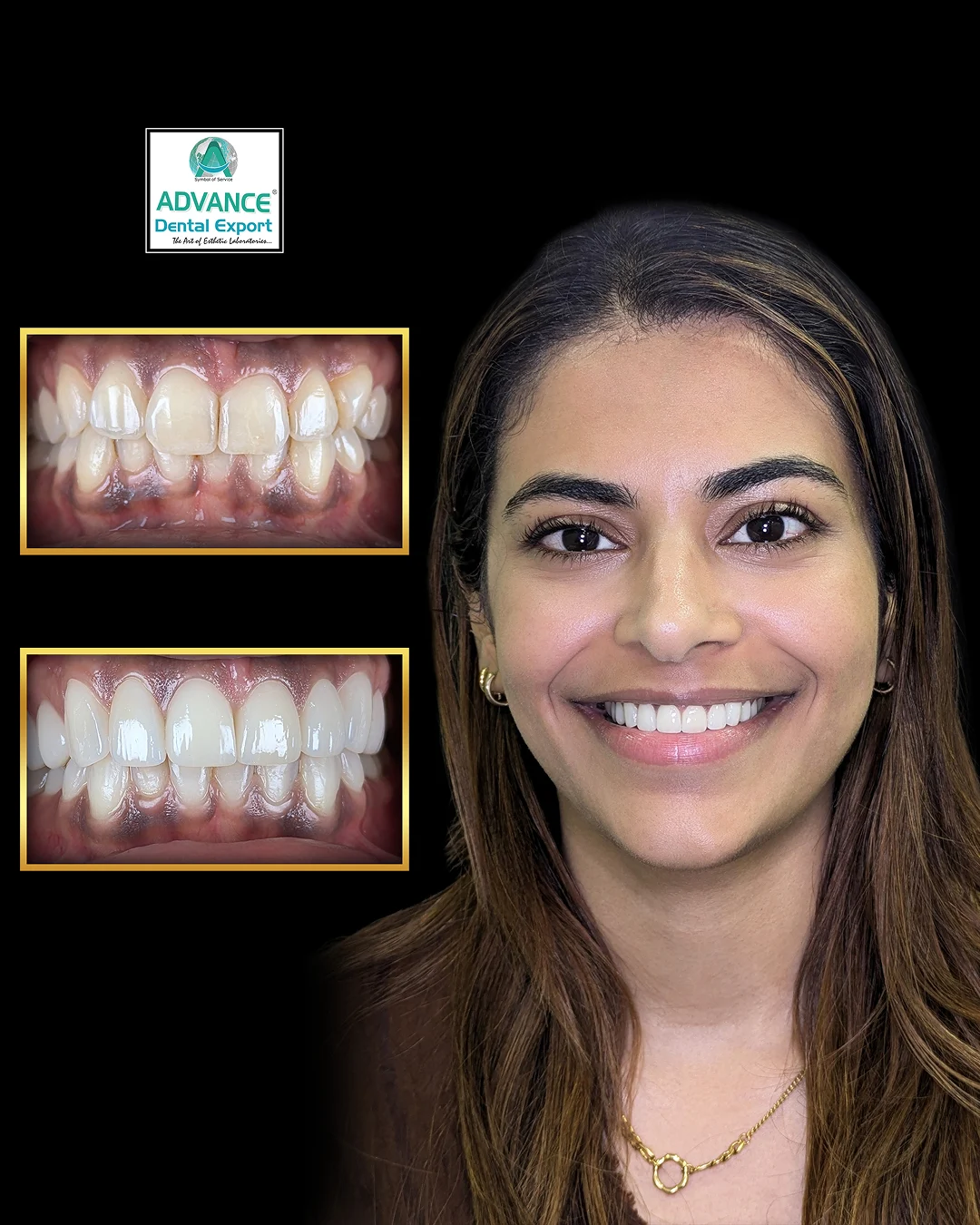
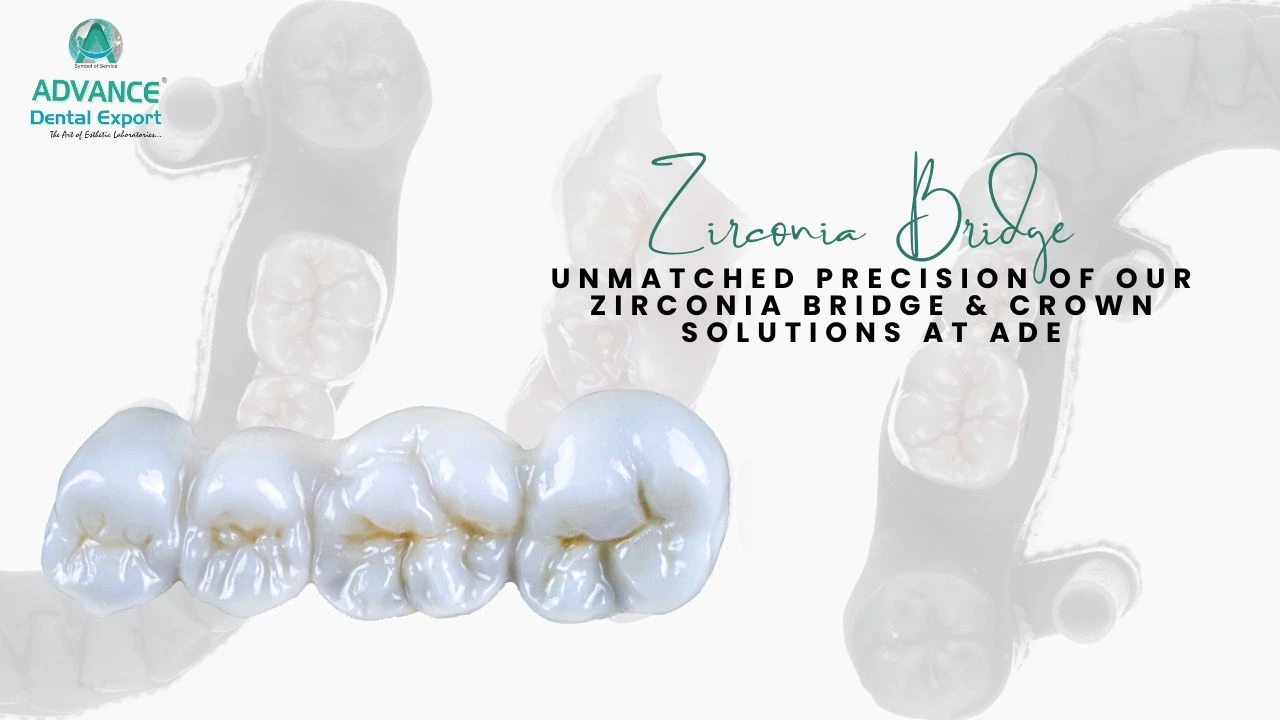
Zirconia crowns have transformed restorative dentistry by offering a versatile solution across various clinical scenarios—from single-unit restorations to implant-supported full arches. Yet many dentists struggle to match material choice to specific treatment needs, leading to unnecessary remakes or compromised outcomes.
Have you ever questioned whether zirconia is right for that pediatric patient or demanding bruxer? Let’s explore the specific applications of zirconia crowns where it excels—and how to implement them effectively in your dental practice.
Overview of Zirconia Crowns in Modern Dentistry
Zirconia crowns leverage the exceptional properties of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), a material originally developed for aerospace applications before its adoption in dentistry. Modern dental zirconia is fabricated via CAD/CAM milling of pre-sintered blocks, followed by high-temperature sintering to achieve final strength and dimensions. There are three principal types of zirconia crowns—monolithic (solid), layered (veneered), and high-translucent variants—each designed to balance translucency with mechanical performance. Recent material classifications include fully stabilized cubic, partially stabilized zirconia, and tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline forms, tailored for specific clinical indications.
Applications of Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns serve as a versatile solution across a spectrum of restorative scenarios, from individual tooth repairs to full-arch rehabilitations. Their applications include single-tooth restorations, multi-unit bridges, implant-supported prostheses, pediatric restorations, cosmetic smile makeovers, bruxism management, and reinforcement of endodontically treated teeth.
By integrating zirconia and digital workflow compatibility into each use case, clinicians can streamline treatment protocols and elevate patient satisfaction. Let’s explore each application in detail:
Single-Tooth Restorations
Zirconia crowns are highly effective for single-tooth restorations due to their precise marginal fit and strength. The use of CAD/CAM technology in fabricating pre-sintered zirconia blocks allows for excellent accuracy, which minimizes the need for adjustments during placement.
Clinical studies have demonstrated survival rates exceeding 95% over 10 years for zirconia single crowns, with very low incidences of complications such as chipping or debonding. Its high flexural strength, ranging from 900 to 1,200 MPa, combined with chemical inertness, ensures that zirconia crowns can withstand the demanding forces of mastication while maintaining excellent aesthetics in both anterior and posterior regions.
According to some resources and guides related to zirconia crowns , the biocompatibility of zirconia reduces inflammation risk, contributing to healthier surrounding tissues and longer-lasting restorations.
Explore Our Restorations
Multi-Unit Bridges
Monolithic zirconia is a popular choice for multi-unit bridges because it provides superior strength without requiring a metal substructure. The connector cross-sectional area can be designed as small as 9 mm² while still resisting fracture and bending forces. This design flexibility allows for streamlined fabrication of 3- to 4-unit bridges with minimal risk of failure.
Compared to porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) , zirconia bridges show fewer issues with veneer chipping, mainly because they often use monolithic (full-contour) zirconia without veneering porcelain. Digital workflows facilitate precise design, enabling excellent passive fit on multiple abutments, which reduces intraoral adjustments and improves patient comfort. Additionally, the lighter color of zirconia bridges enhances esthetics, especially in cases where metal frameworks might show through.
Implant-Supported Prostheses
Zirconia crowns on implants have become increasingly popular for their ability to be custom-milled as both abutments and crowns. This custom fabrication allows for optimal emergence profiles, which support healthy soft tissue and natural-looking gingival contours. Zirconia’s biocompatibility minimizes inflammatory responses around the implant site, contributing to better long-term peri-implant tissue health.
CAD/CAM milling ensures an extremely precise fit at the implant-abutment junction, which helps prevent microgaps that could harbor bacteria. Clinical data shows stable soft tissue integration and high patient satisfaction with zirconia implant restorations, highlighting their reliability and esthetic advantages over traditional metal abutments .
Full-Arch Reconstructions
Full-arch rehabilitations, such as “All-on-4” or “All-on-6” prostheses, benefit from monolithic zirconia frameworks due to zirconia’s superior strength and durability. These prostheses can withstand significant masticatory forces while maintaining esthetic appeal by using multilayered zirconia blocks that provide natural shading and translucency gradients. Compared to acrylic-veneered prostheses, zirconia frameworks demonstrate fewer mechanical failures and reduced maintenance visits.
The digital design process allows clinicians and technicians to customize occlusal schemes and anatomic features to each patient’s unique oral environment, leading to improved function, comfort, and speech. This customization also reduces chair time by minimizing the need for intraoral adjustments.
Pediatric Dentistry Applications
In pediatric dentistry, prefabricated zirconia crowns have become a preferred alternative to traditional metal crowns. They provide full-coverage restoration of primary teeth while addressing common aesthetic concerns of parents and children due to their tooth-colored appearance. The smooth, biocompatible surface of zirconia crowns reduces gingival irritation and inflammation post-placement, improving patient comfort and oral health outcomes.
Available in a range of sizes to fit various pediatric arch forms, zirconia crowns simplify inventory management and chairside selection. Their durability also means fewer replacements and less trauma for young patients, which is important for maintaining positive dental experiences early on.
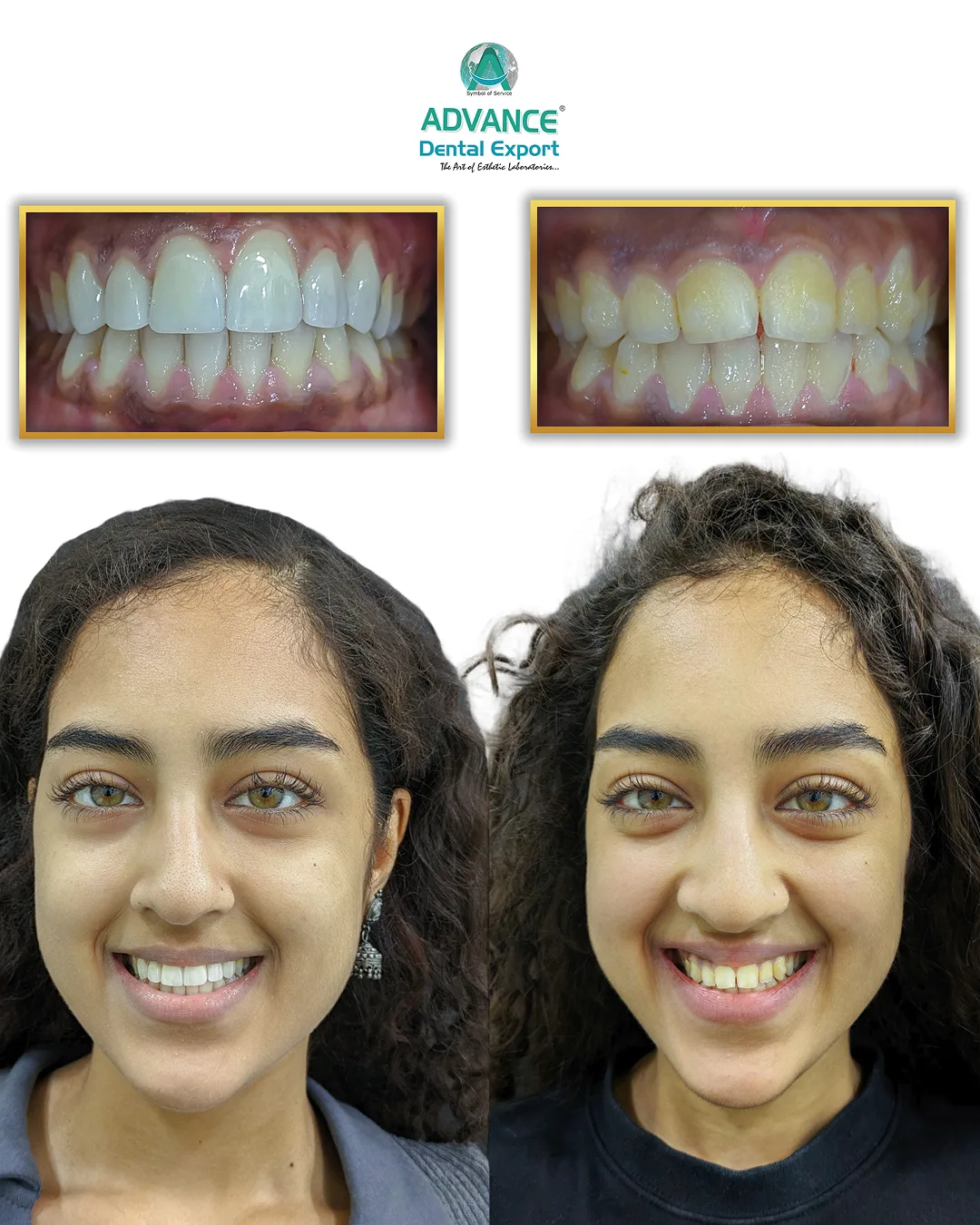
Cosmetic Enhancements
Zirconia crowns are widely used for cosmetic dental treatments where subtle reshaping and esthetic improvement are required. Their ability to mimic natural tooth anatomy and color is enhanced by the availability of layered or gradient zirconia blocks that allow for precise control over translucency and shade.
Looking for a trusted lab partner? Get high-precision restorations from Advance Dental Export
Digital shade mapping and 3D printing further optimize the color match and surface texture, enabling highly predictable and lifelike results. These crowns allow clinicians to improve smiles without aggressive tooth reduction, preserving more natural tooth structure while achieving desired esthetic outcomes. The stability of zirconia under oral conditions also ensures that the cosmetic improvements are long-lasting and resistant to discoloration.
Management of Bruxism
Patients with bruxism present a challenge due to the excessive forces they place on restorations. Zirconia crowns are especially suited for managing these cases because of their high fracture toughness and wear resistance. Monolithic zirconia restorations can withstand occlusal forces often exceeding 800 N without chipping or fracturing, protecting both the crown and opposing dentition.
Customized occlusal designs can be milled precisely into the zirconia surface to evenly distribute forces and reduce localized stress points. This durability reduces the frequency of restoration failures and maintenance appointments in patients with parafunctional habits, making zirconia a practical choice for long-term success.
Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth
Zirconia crowns are ideal for restoring endodontically treated teeth, which typically require full-coverage to protect weakened structures. These crowns allow for conservative tooth preparation with axial reductions between 1.0 and 1.5 mm, preserving as much natural tooth as possible while providing robust protection against fracture.
The endocrown technique, where a monolithic zirconia restoration extends into the pulp chamber, offers an alternative to traditional posts and cores by simplifying the restorative process. This method improves retention and fracture resistance while minimizing cement space and marginal gaps. Clinical outcomes show high success rates, with minimal incidence of marginal leakage or secondary decay, reinforcing zirconia’s role as a dependable restorative material for compromised teeth.
Conclusion
From single-unit repairs to full-arch rehabilitations, zirconia crowns fit into every restorative workflow with remarkable precision and minimal adjustments. They serve diverse needs—from implant-supported prostheses and pediatric restorations to cosmetic makeovers, bruxism cases, and endocrown solutions—without altering core protocols. By leveraging CAD/CAM accuracy and dental crown material versatility , these crowns streamline practice operations and broaden treatment options for clinicians and patients alike.